Water Quality Basics
Water is an essential component of life. Every living organism on earth, from bacteria to humans, must have water in some form in order to survive.
Having a reliable supply of clean water is important for our health, the environment and recreational activities. Water provides food, water and shelter for plant and animal communities. We also use water to produce electricity, grow food, wash our clothes, for recreation and much more.
Distribution and Movement of Water
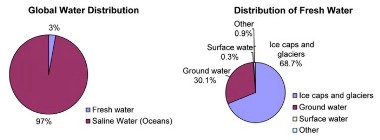
While water covers 75% of the earth’s surface, very little of this water is readily available to humans. We require fresh water for drinking, as well as for many of our activities such as growing food and watering livestock. However, fresh water makes up only 3% of the water on the earth’s surface. Of this 3%, only 0.3% is easily accessible, with much of the fresh water being contained in ice caps, glaciers and as groundwater.
The total amount of water on earth is constant; however, water is always moving and changing forms. This means that the water you drank at breakfast may have fallen as rain half way around the world a year ago, or may have been used by a dinosaur 100 million years ago. Because the water that we have today is the same water that we will have tomorrow and one hundred years from tomorrow, it is important that we take good care of what we have.
The continuous movement of water is known as the hydrologic or water cycle.
What influences water quality?
Water quality can be affected by many factors within a watershed, including climate, landscape and human activities.
The vegetation, geology and hydrology of an area can have a dramatic impact on surface water quality. For example, the water of a fast moving mountain stream will be much different then a slower moving prairie stream.
Human activities can also influence water quality.
Rain can wash materials from our landscape, such as soil, salt, fertilizers and pesticides into our waterways. Altering the landscape, through such things as logging, agriculture and road construction may also impact the health of our waterways. In this way both urban and rural land uses can have a dramatic influence on water quality.
While we can’t eliminate all of our sources of water contamination and disturbances, we can take steps to educate ourselves and reduce our impacts.
Water Quality Monitoring
There is no single or simple measure of water quality. Water quality is evaluated differently depending on what the ultimate use of the water is. For example, water quality may be evaluated based on:
- aquatic life
- drinking water
- recreation
- agricultural uses
When testing water quality, we can focus on three broad categories:
Physical characteristics: such as temperature, colour, suspended solids and turbidity
Chemical characteristics: such as nutrients, minerals, metals, oxygen, and organic compounds
Biological characteristics: such as the types and quantities of aquatic plants, animals, algae, bacteria and protozoan parasites.
During AWQA Day, we focus on the first and second categories: physical and chemical characteristics. By looking at temperature, dissolved oxygen, pH and turbidity we are measuring water quality characteristics that can have important implications for fish and wildlife habitat, outdoor recreation and human health.
More Information




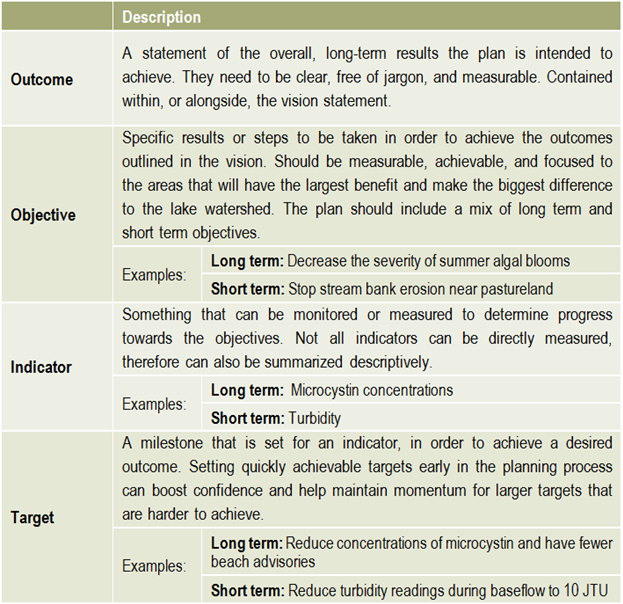
 The members of the steering committee will continue to play a strong role in facilitating and tracking implementation actions. This includes any actions they were responsible for, as well as tracking other committees and sector’s actions and progress made towards achieving the plan’s outcomes. Ongoing communication is essential to successful implementation and achieving outcomes, therefore a regular reporting mechanism could be set up in order to provide regular evaluation of the plan.
The members of the steering committee will continue to play a strong role in facilitating and tracking implementation actions. This includes any actions they were responsible for, as well as tracking other committees and sector’s actions and progress made towards achieving the plan’s outcomes. Ongoing communication is essential to successful implementation and achieving outcomes, therefore a regular reporting mechanism could be set up in order to provide regular evaluation of the plan.

 Reporting is an essential component of any watershed management planning and implementation process. There are two main types of reporting that should be shared with stakeholders on a regular basis: implementation reporting & effectiveness reporting.
Reporting is an essential component of any watershed management planning and implementation process. There are two main types of reporting that should be shared with stakeholders on a regular basis: implementation reporting & effectiveness reporting.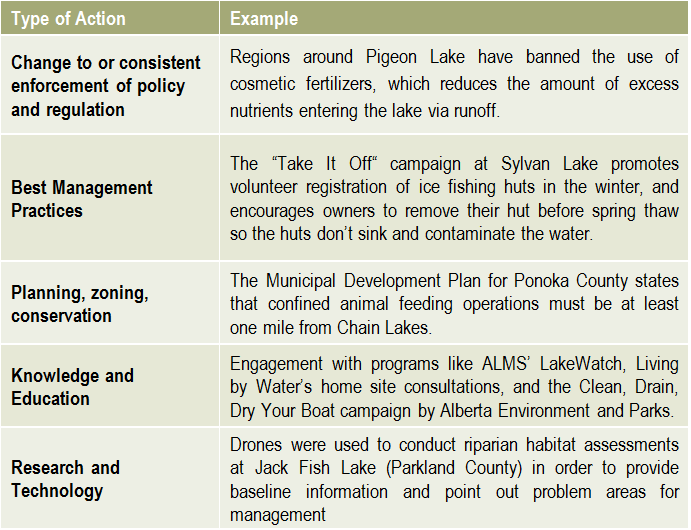 There is no limit to the number or types of lake management actions, but they typically fall into the categories on the right.
There is no limit to the number or types of lake management actions, but they typically fall into the categories on the right.

 Helpful resources
Helpful resources The development of a lake watershed management plan provides the guidance needed to implement activities, but the plan cannot be static. Monitoring the performance of your management actions is essential to understanding whether your goals have been met, and whether further actions are needed. Monitoring and evaluating the implementation and effectiveness of a lake watershed management plan allows assessment of progress towards the goals and objectives of the plan, identification of problems and opportunities, and a collection of critical information required when performing a 5 or 10 year review of the plan.
The development of a lake watershed management plan provides the guidance needed to implement activities, but the plan cannot be static. Monitoring the performance of your management actions is essential to understanding whether your goals have been met, and whether further actions are needed. Monitoring and evaluating the implementation and effectiveness of a lake watershed management plan allows assessment of progress towards the goals and objectives of the plan, identification of problems and opportunities, and a collection of critical information required when performing a 5 or 10 year review of the plan.
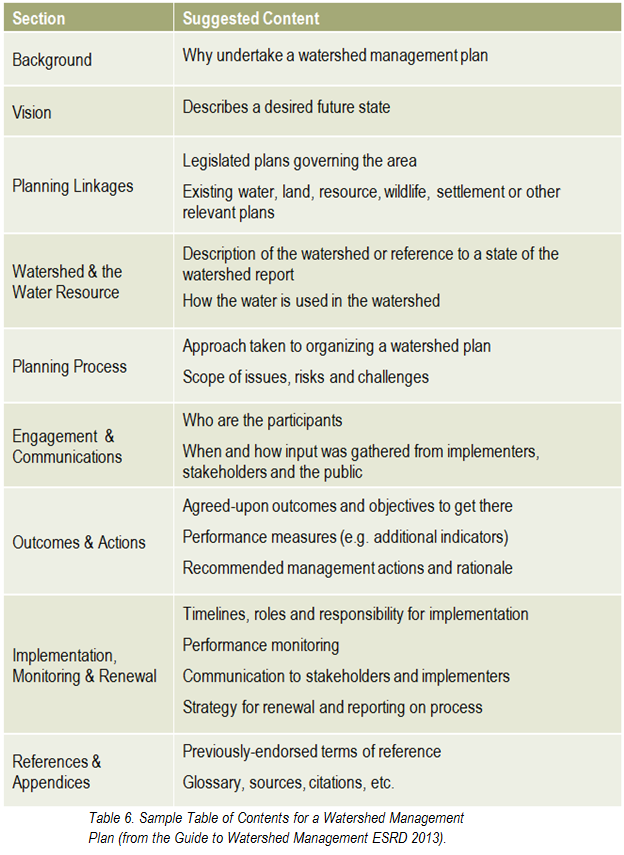
 What has the monitoring results of the plan and of the indicators shown? Is there a need to modify the plan? It is important that the lake watershed management plan does not just sit on a shelf. Information gaps should be addressed, action items need to be managed, completed, and evaluated to best address the needs of the lake. Always keep in mind the vision: if the actions taken are not bringing the lake closer to that vision, then the plan needs to be modified. Consider updating both the state of the watershed and the lake watershed management plans at regular intervals to make sure that the actions taken were achieving the desired outcomes and to evaluate what work still needs to be done.
What has the monitoring results of the plan and of the indicators shown? Is there a need to modify the plan? It is important that the lake watershed management plan does not just sit on a shelf. Information gaps should be addressed, action items need to be managed, completed, and evaluated to best address the needs of the lake. Always keep in mind the vision: if the actions taken are not bringing the lake closer to that vision, then the plan needs to be modified. Consider updating both the state of the watershed and the lake watershed management plans at regular intervals to make sure that the actions taken were achieving the desired outcomes and to evaluate what work still needs to be done.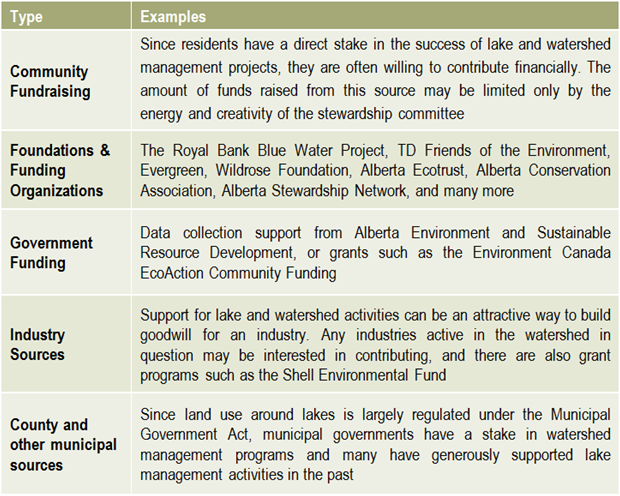 Once a plan has been approved by all affected sectors and officially endorsed and released by the steering committee, then implementation can begin in full. Action projects can be large and comprehensive, or made smaller by staging projects over time or into modules that can be tackled one at a time. Fundraising is an issue that many community groups may find intimidating, but experience with programs such as the Pine Lake Restoration Program (see
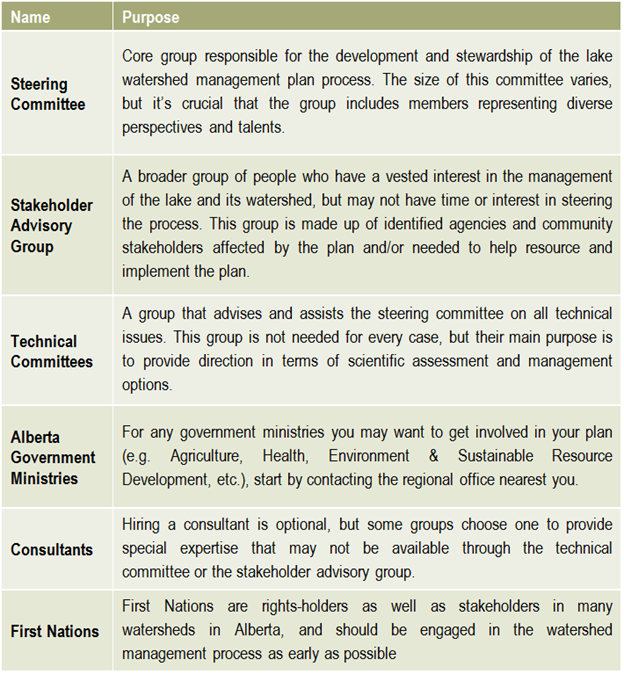
Once a plan has been approved by all affected sectors and officially endorsed and released by the steering committee, then implementation can begin in full. Action projects can be large and comprehensive, or made smaller by staging projects over time or into modules that can be tackled one at a time. Fundraising is an issue that many community groups may find intimidating, but experience with programs such as the Pine Lake Restoration Program (see 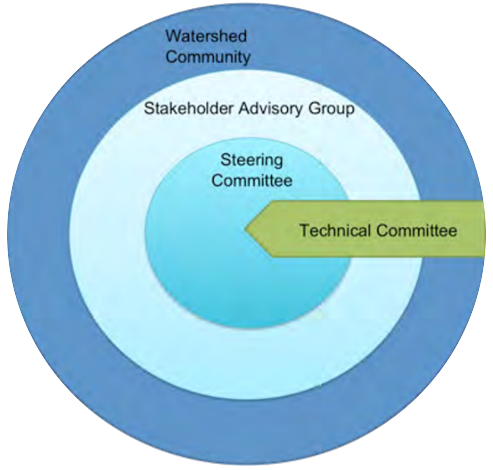 This graphic describes how the various committees and groups will work and interact together. The circle size depicts the approximate number of people involved, and the circles overlapping indicates that some individuals may reside in all of the circles and participate in multiple committees as part of the planning process. The technical committee is shown as an arrow, indicating that it is independent and has relatively few people, and yet it interacts with all of the groups. This graphic may look different depending on the lake and the people involved, and a detailed structure should be agreed upon and described in the plan’s Terms of Reference (Step 6).
This graphic describes how the various committees and groups will work and interact together. The circle size depicts the approximate number of people involved, and the circles overlapping indicates that some individuals may reside in all of the circles and participate in multiple committees as part of the planning process. The technical committee is shown as an arrow, indicating that it is independent and has relatively few people, and yet it interacts with all of the groups. This graphic may look different depending on the lake and the people involved, and a detailed structure should be agreed upon and described in the plan’s Terms of Reference (Step 6).